作業系統筆記 Introduction
周志遠教授作業系統開放式課程
Computer System
- 由 Hardware、OS、Application、User 組成
- User:people、machines
- Application:使用 system resources 來解決問題的方式,像是各種軟體
- Operation System:controls 與 coordinates 資源的使用
- Hardware:提供基本的計算資源(CPU、memory、IO devices)
What is an Operation System
- Permanent Software
- 電腦啟動後永遠存在,沒有它電腦就不會運作
- Abstracts 硬體資源給使用者使用
- 把底層的各種資源變成一堆 API,給使用者方便使用,virtual 的概念
General-Purpose Operating Systems
- Linker 會 link System Library,裡面有一堆 System call 的 API
- 使用 printf 的時候要印到螢幕,是 OS 負責的,所以要 system call
- user 呼叫 printf -> printf 呼叫 system call -> system call 呼叫 driver…
- Device drivers 是 OS 的一部分
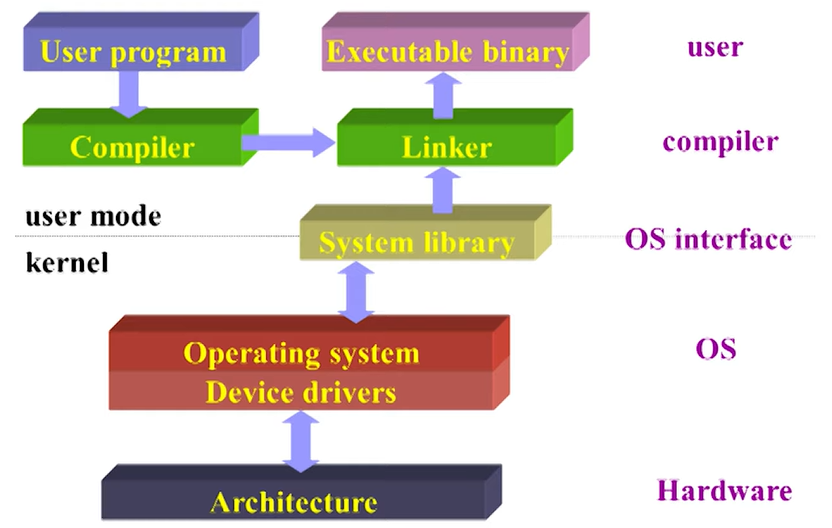
OS 的定義
- Resource allocator
- manages 和 allocates resources 來確保公平性和效率
- Control program
- controls 程式的執行 (driver) 和 IO devices 的操作
- Kernel
- OS 又稱為 Kernel
OS 的目的
- 方便性 (convenience)
- 像是 windows 的崛起,也就是發展出圖形介面,讓使用者更方便操作
- 效率 (Efficiency)
- 更有效率的使用資源,當問題很複雜時,Efficiency 是最後追求的東西
- 像是很多人用 Linux,是因為圖形介面也會吃資源,但那不是必要的
- 兩者衝突,追求方便性效率就下降,追求效率方面性就下降
OS 的重要性
- OS 是 user program 和 hardware 之間 唯一 的 interface,一定需要經過它
- OS 絕對不能有 bug,一旦 crash 掉整台電腦就掛了
- OS 和電腦的架構息息相關,因此隨著需求不同,也發展出形形色色的 OS
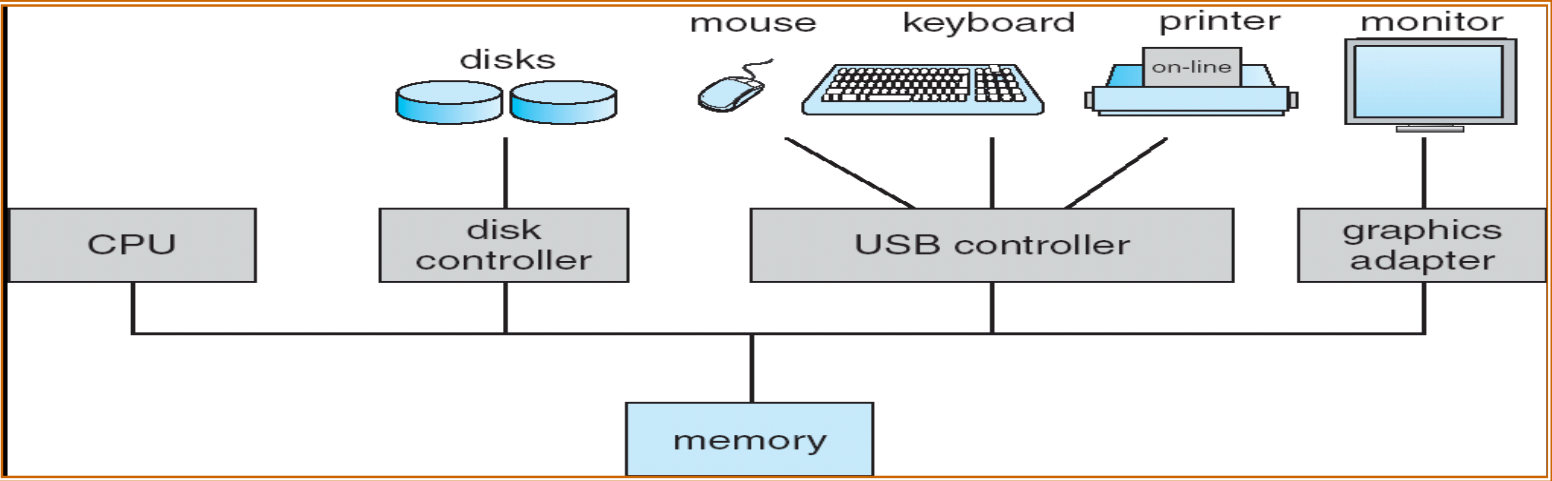
Computer-System Organization
- 由一個 Bus 連接 CPU、Memory、IO Device 等,作業系統就負責 Control 和 Coordinate
Device Controller (Hardware)
- 負責控制最 low level 的硬體,每個 Device 會有一個 Device Controller 來做溝通
- Status reg 用來記錄現在 device controller 是 busy 還是 idle
- Data reg 和 buffer 都是用來存資料,會先寫到 reg 再寫到 buffer
- CPU 下指令後,Device controller 就能夠去 access disk 資料到自己的 local buffer
- Memory 是 CPU 在用的,所以 CPU 負責 移入/ 移出 memory 的資料到 Device Controller 上的 local buffer
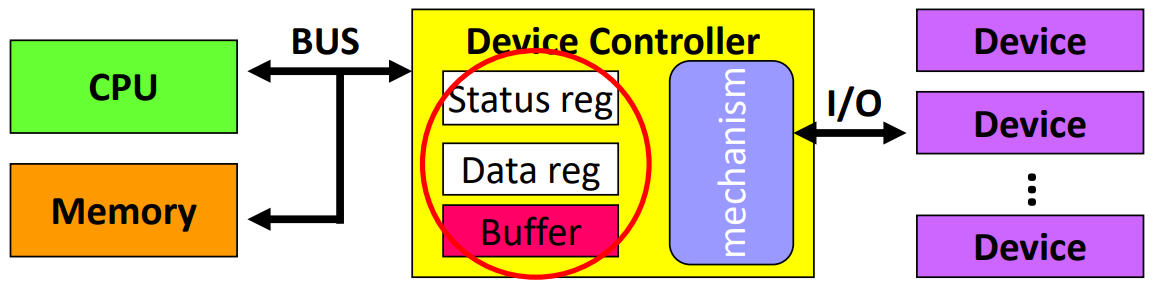
由於 Device Controller 上的 Buffer 空間是有限的,因此會需要用一些技巧來解決,像是 Busy/ wait、Interrupt
Busy/wait output
- 最簡單暴力的運行方式,但是很浪費 CPU,CPU 變成用來監控 Buffer
1 | |
Interrupt I/O
- 原本 CPU 在執行某程式碼,Interrupt 可以打斷這件事情,要求 CPU 先做其他事情,做完之後再回去執行原本的程式碼
- 現在的作業系統都是這種形式
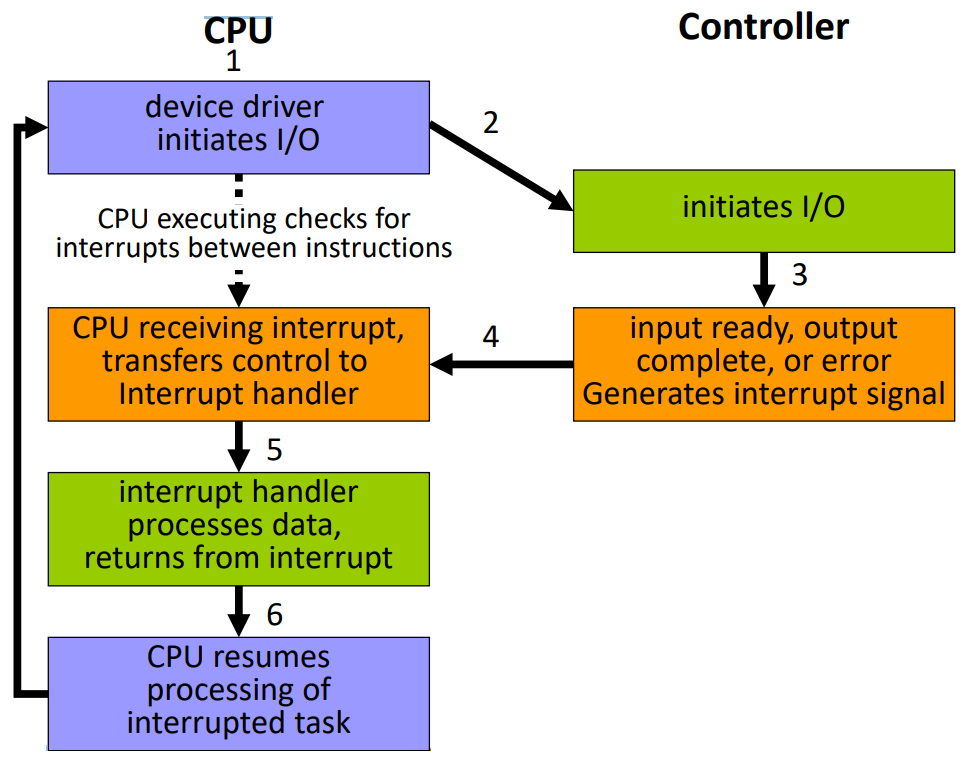
又可以分成 Hardware 和 Software
Hardware Interrupt
- 又稱為 Signal
Interrupt Service Routine
- interrupt vector 是 array of function pointers,array 大小是固定的
- 因為每個 function 的程式碼大小不同,所以這邊用指標來儲存,每個欄位是 4 bytes
- signal 都會有一個 singal number,根據這個 number 去找 vector 上的欄位
- 每個 port 的 hardware 有燒死的 singal number, 裝 driver 的時候會 overwrite 那個欄位的 fucntion pointer 的位置,去執行你要處理的程式碼
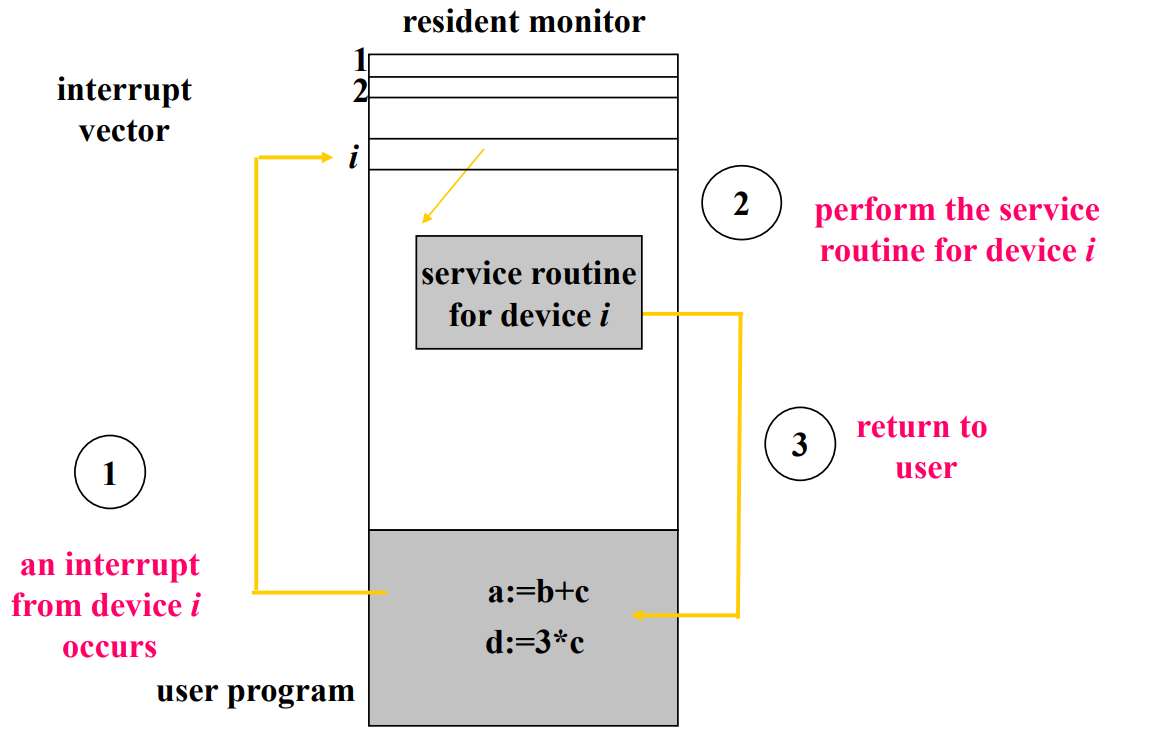
Softwarae Interrupt
- 又稱為 Trap
Interrupt Service Routine
- 是用 switch case 而不是 array,因為軟體有無限的可能性,可以任意定義各種不同的 system call
- 流程跟 hardware interrupt 差不多,根據 system call 的 number 來去找尋對應的 function call
- 通常是使用者的程式去 Trigger 的,又可以分成主動和被動
- 主動,也就是去 call System Call
- 被動像是出現 Error 的時候要處理
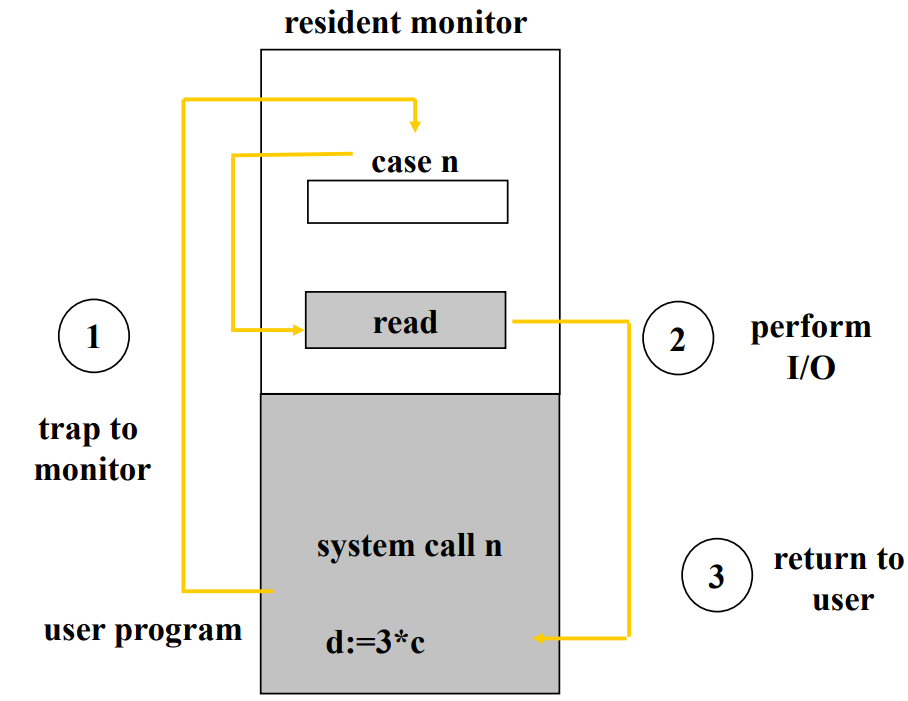
不管是 Hardware Interrupt 或是 Software Interrupt,Interrupt 的時候必須記得被打斷的程式的 Instruction Address,才能再處理完 Interrupt 回去繼續執行。
有時候 Interrupt 還會有 Hierachy,像是有時候動滑鼠會沒有反應,是因為它卡在某 Interrupt routine 裡面,所以沒有處理到滑鼠的 Interrupt
Storage-Device Hierarchy
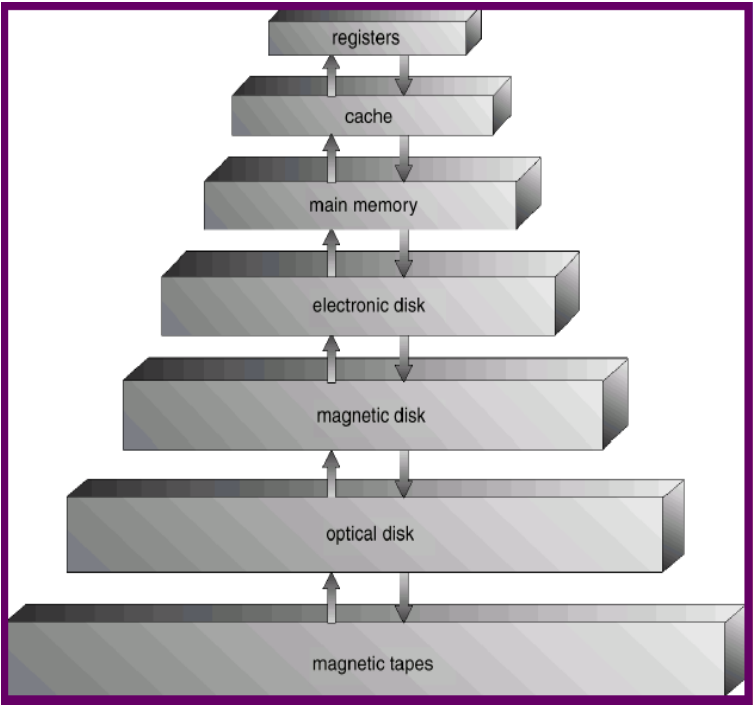
- 真正的大型的系統最後還是用 tapes,因為非常 reliable,不太容易壞,而且很便宜
- 這是最傳統的架構,現在有很多其他的 storage device 會插在中間
- 要考量的點
- speed, cost, volatility
- volatile 關掉會遺失,memory 以上的全部都是 volatile
- Main memory 是 CPU 能夠直接 access 的唯一大型的 storage
- Secondary storage
- memory 以下都叫做 secondary storage,代表 CPU 沒辦法直接讀取
- 是大型的 non-volatile 的 storage
Random-Access Memory
DRAM (Dynamic RAM)
- one transistor
- less power
- must be periodically refreshed
- 體積小,速度比較慢
- 因為 CPU 有很多 core, RAM 的速度其實就那樣,channel 的 bus 其實才是真正的 bottleneck
- Main Memory
SRAM (Static RAM)
- six transistors
- more power
- Cache Memory
Random Access 重要的地方是,你讀取任何位置的資料,時間都是一樣的,才能確保每次執行的結果相同,如果不一樣的話使用者會很難控制電腦
Disk Mechanism
- 讀取的時間跟資料的位置有關係
- 速度計算
- Transfer Time = data size / transfer rate
- Positioning Time = Seek Time (Cylinder) + Rotational Latency (Sector)
- 如果是連續資料的讀取,其實 Hard Drive 並不會輸 SSD
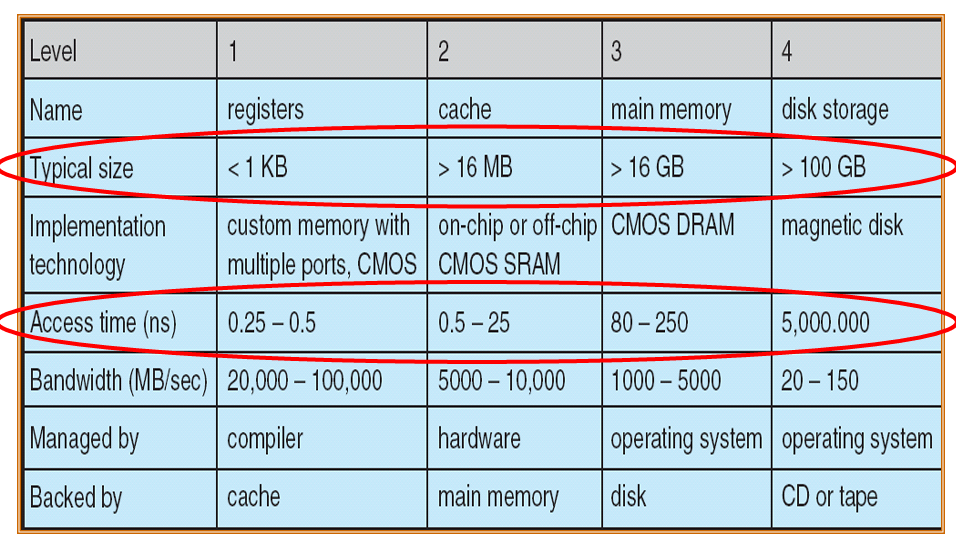
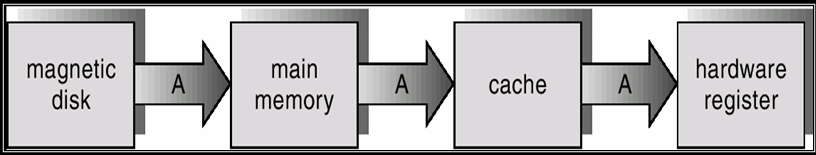
Caching
- 把速度比較慢的 Storage 複製到速度比較快的 Storage
- 如果這層找不到資料,會一層一層往下檢查,直到找到,所以有時候會比沒有 Caching 還慢
Coherency and Consistency Issue
對資料做修改時,如果 Cache 修改資料時沒有更新到 Memory,其他程式在讀取時,會發生這種問題。像是 Multi-Core Processor 就會需要去處理,因為大家的 L1 Cache 是不同的,但是 L2、L3 相同
Single task accessing
- 基本上沒問題,只會用到最上層的
Multi-task Accessing
- 要處理大量這類的問題
Distributed System
- 更加複雜,還要考慮到網路的問題
Hardware Protection
不是指 Security (網路攻擊、惡意攻擊),指的是很多程式在執行,或是很多使用者在執行時,不會影響彼此,像是 Memory 的內容只有我自己能夠讀取,其他使用者無法讀取
Dual-Mode
- 藉由 Hardware Support 來做最基本的 Protection,其他軟體會基於 Hardware 來實現 Protection
- User Mode - 來自使用者執行的程式
- Monitor Mode (Kernel Mode) - 來自 OS 執行使用者的程式
- Call Interrupt 時,它知道你正在用 System Call,所以它會把 Mode bit 變成 0 (Kernel Mode),沒有的話就是 1 (User Mode)
Priviledge Instructions
- 必須在 Kernel Mode 才能執行的 Instruction,如果他發現 Mode bit 是 1,它會告訴 OS,送給你一個 fault
- 保護電腦,不然使用者隨便寫個 Instruction 送到 CPU 就可以控制硬體
I/O Protection
- 每個 I/O Instructions 都是 Previledge Instructions,都要透過 OS
- 早期有個 Bypass Hack 的方式,也就是去改寫 Interrupt Vector 裡面的值,所以 OS 就能去執行我自己想要的程式碼
Memory Protection
- Protect
- 要保護 Interrupt Vector、Interrupt Service Routines
- 不能 Overwrite 別人的程式碼
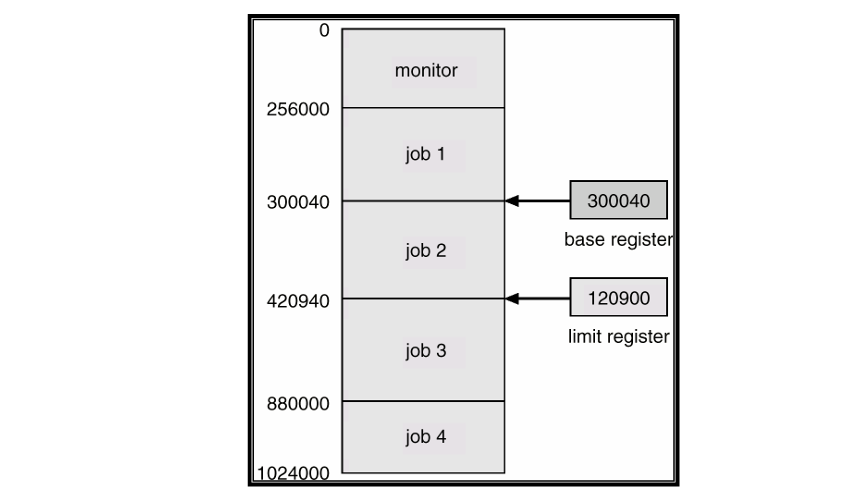
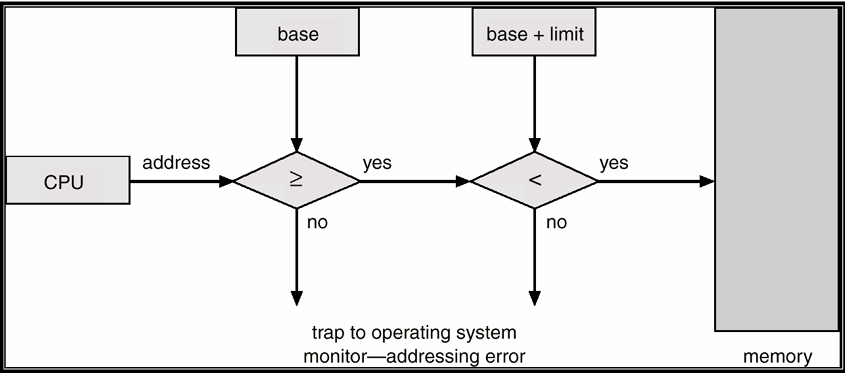
- Haredware Support: 使用兩個 register 來記錄能夠讀取的記憶體區間
- Base register: 開始的位址
- Limit register: 這段佔記憶體多長
- 超過這段空間就會有 Segmentation Fault
- 修改 Base register 和 Limit register 都是 Priviledge Instructions
CPU Protection
- 阻止某隻程式霸佔 CPU,像是無窮迴圈
- Hardware Support: Timer
- Timer 是慢慢減少,當變成 0 時,會送出 Interrupt
- Timer 通常用來實現 Time Sharing
作業系統筆記 Introduction
https://933yee.github.io/notes/2024/07/09/os-chapter1/