AIAS - Basic
Lecture
Base Conversion
可以直接用 gdb 來看數字的表示方式,例如1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8(gdb) p/t 43275
$1 = 1010100100001011
(gdb) p 0b1010100100001011
$2 = 43275
(gdb) p/x 43275
$3 = 0xa90b
(gdb) p 0xa90b
$4 = 43275這樣就可以看到 43275 的二進位、十進位、十六進位表示方式。
Digital & Analog
- Quantization: 把類比轉成數位訊號。
會先在時間軸上做 Sampling,再對 Sample 出的訊號強度做數值 Mapping。
- Quantization: 把類比轉成數位訊號。
Lab
Python
C/C++
Bitwise Operation
多用 bitwise 增加 readability 和 performance。
1 | |
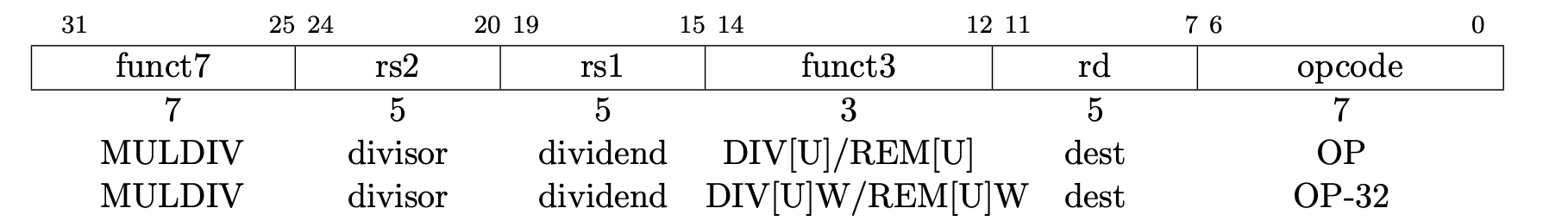
BIT_MASK(start, end)會產生從 start 到 end 都是 1 的 mask(~0U) >> (31 - (start))會產生從 start 和 start 之後的 bit 都是 1 的 mask~((1U << (end)) - 1)會產生 end 之後的 bit 都是 0 的 mask
方便對以下做 decode
Valgrind
C 語言沒有 garbage collection,記憶體要自己控制,可以用 valgrind 來檢查記憶體是否有釋放。
編譯時要加上
-g參數,才能看到程式碼的行數。
1 | |
Valgrind 訊息可以分成幾種:
definitely lost: 直接遺失,程式完全無法訪問這塊記憶體1
2
3
4
5#include <stdlib.h>
int main() {
int* ptr = malloc(10 * sizeof(int));
return 0;
}1
2
3
4
5==346== definitely lost: 40 bytes in 1 blocks
==346== indirectly lost: 0 bytes in 0 blocks
==346== possibly lost: 0 bytes in 0 blocks
==346== still reachable: 0 bytes in 0 blocks
==346== suppressed: 0 bytes in 0 blocksindirectly lost: 因為其他記憶體被洩漏而無法釋放1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20#include <stdlib.h>
typedef struct Node {
int value;
struct Node *next;
} Node;
void leak_linked_list() {
Node *head = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
head->next = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
head->next->next = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
head->next->next->next = NULL;
free(head);
}
int main() {
leak_linked_list();
return 0;
}1
2
3
4
5
6==334== LEAK SUMMARY:
==334== definitely lost: 16 bytes in 1 blocks
==334== indirectly lost: 16 bytes in 1 blocks
==334== possibly lost: 0 bytes in 0 blocks
==334== still reachable: 0 bytes in 0 blocks
==334== suppressed: 0 bytes in 0 blockspossibly lost: 有奇怪的操作,valgrind 也不確定這塊記憶體是不是真的loststill reachable: 記憶體在程式結束時仍然可訪問,但沒有 free 掉1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12#include <stdlib.h>
int *global_ptr;
void still_reachable_memory() {
global_ptr = (int *)malloc(10 * sizeof(int));
}
int main() {
still_reachable_memory();
return 0;
}1
2
3
4
5
6==406== LEAK SUMMARY:
==406== definitely lost: 0 bytes in 0 blocks
==406== indirectly lost: 0 bytes in 0 blocks
==406== possibly lost: 0 bytes in 0 blocks
==406== still reachable: 40 bytes in 1 blocks
==406== suppressed: 0 bytes in 0 blocks
Verilog
- Combinational Circuit
輸出只取決於當前的輸入,與電路中的狀態無關。根據 input signal 的組合,直接計算出 output signal 的邏輯函數,過程中不會有任何的 memory。
- Sequential Circuit
輸出不僅取決於當前的輸入,還取決於電路中留存的狀態。在 combinational circuit 的基礎上,加入了 memory 元件,例如 flip-flop。
Verilog Syntax
Data Type
wire: 用來連接不同的元件,只能用來連接output和input,沒有特別註明的話,預設就是wire。reg: 用來儲存state,可以用來儲存output。- 對於
module內部而言,input 只能用wire連接,output 可以用wire或reg連接。 - 對於
module外部而言,input 可以用wire或reg連接,output 只能用wire連接。
- 對於
當 wire 沒有被 assign 時,預設值為 **X(Unknown)**,當 reg 沒有被 assign 時,預設值為 **Z(High Impedance/ Floating)**。
Vector
[MSB:LSB] 或 [LSB:MSB] 都可以
1 | |
Array
要把宣告的 Dimension 寫在變數名稱的後面
1 | |
Data Assignment
在 HDL 如 Verilog 中最常使用到的表示方法通常是 2 進制以及 16 進制,不過為了方便也可以用 10 進制表示。另外可以加上 _ 來增加可讀性。
1 | |
Dataflow Level
Data assignment
assign LValue = RValue
LValue 只可以是wire,但是 RValue 可以是wire或是reg- 通常用在 assign module output port
Concatenation operator
LValue = {Concat0, Concat1, ...}Concat0,Concat1可以是wire、reg或直接寫數字,像是8'b1010_1010
Replication operator
LValue = {N{Pattern}}1
2
3wire [31:0] combine;
assign combine = {3{in0}, 2{in1}, 12'hfaa};
// combine = 00_in0_in0_in0_in1_in1_1111_1010_1010
Behavior Level
主要就是用 always block,但裡面的 Data Assignment 只能對 reg 進行操作,Combinational Circuit 或 Sequential Circuit 都可以用。
Combinational Circuit
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10module combinational_circuit (
input A,
input B,
output reg C
);
always @(*) begin
// Combinational logic: output Y is the result of ANDing A and B
C = A & B;
end
endmodulealways @(*): 當所有的input有變動時,就會執行always block裡面的內容。- 可以看到
C要用reg宣告,因為always block裡面只能對reg進行操作。
Sequential Circuit
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16module sequential_circuit (
input clk,
input reset,
input data,
output reg out
);
always @(posedge clk or posedge reset) begin
if (reset) begin
// Asynchronous reset: reset out to 0 when reset is asserted
out <= 1'b0;
end else begin
// Sequential logic: out is updated on the rising edge of clk
out <= data;
end
end
endmodulealways @(posedge clk or posedge reset): 當clk或reset有上升沿時,就會執行always block裡面的內容。<=: Non-blocking assignment,用在Sequential Circuit中
Blocking
描述的順序會影響電路執行結果,執行 assignment 時,會按照描述順序逐一執行,下一個 assignment 會等待前一個 assignment 操作完成。1
2
3
4
5
6always @(*) begin
A = 2; // A = 2
B = C; // B = C
C = A; // C = 2
// These assignments will be executed in order
endNon-blocking
Parallel 的進行資料傳遞,描述的順序不會影響電路執行結果。1
2
3
4
5
6always @(posedge clk) begin
A <= 2; // A = 2
B <= C; // B = C
C <= A; // C = A
// These assignments will be executed at the same time
end
Module Connection
1 | |
盡量用 named connection,增加程式碼的可讀性。開心的話也可以用 ordered connection。
其他像是 If Statement、Case Statement 或 ? : 本質上都是 MUX,跟軟體有差