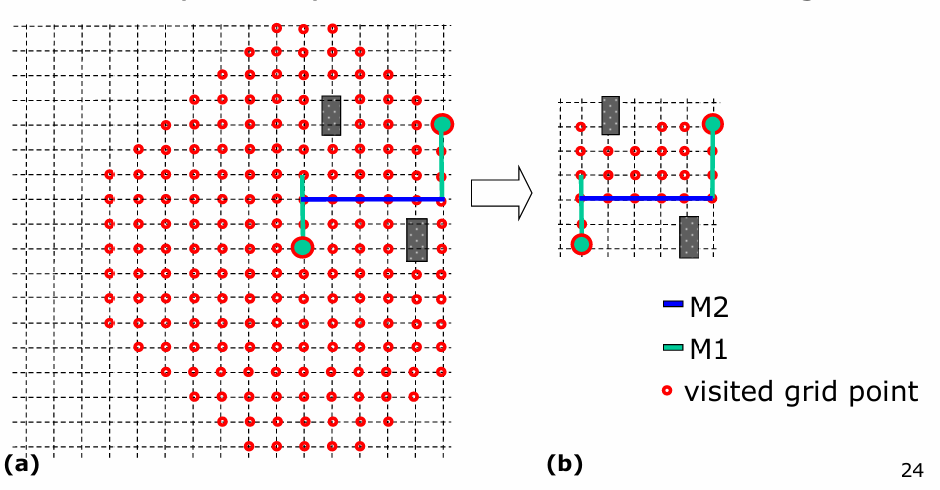
VLSI DFM - Maze Routing
參考清大麥偉基老師課程講義
Lithography
- Lithography: 光刻
框出電路圖案,然後進行蝕刻 - Diffraction: 繞射
會造成 Lithography 不準確,可以從目標圖案反推出 Mask 的設計,稱為 Computational Lithography
- 193i 的
i代表 Immersion Lithography
用液體取代空氣,縮短光的波長,就好像換了一個 Light Source,減少繞射的影響,而且波長 193nm 的技術已經很成熟 - EUV 代表 Extreme Ultraviolet Lithography
波長更短,繞射更少,但是製程更難,因為要用真空,光源也很難做 - Multi-Patterning
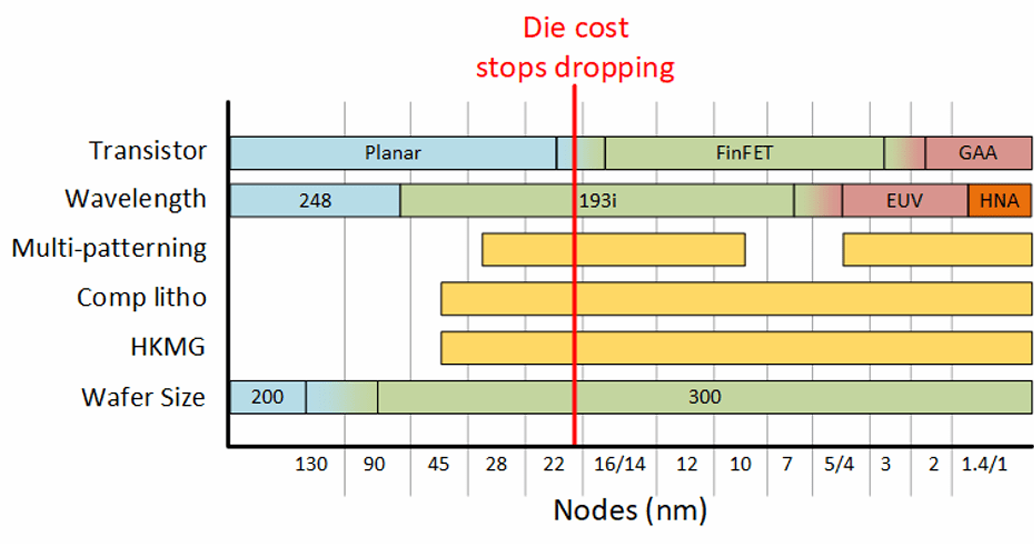
把一個圖案分成多個小圖案,然後分別曝光,最後合併成一個圖案。在 EUV Lithography 之前很常用,現在因為 EUV 很貴,有些先進製程還是用 193i + Multi-Patterning - 隨著技術進步,單位面積上的 Transistor 數量越來越多,但是製程成本也越來越高,所以不是每個裝置都用最先進的製程
Routing in Advanced Nodes
受限於 Lithography printability、Process Variation 等,即使你用一樣的方法,做出來的也不一定是你要的。所以要考慮 Design for Manufacturability。
Design Rule Handling
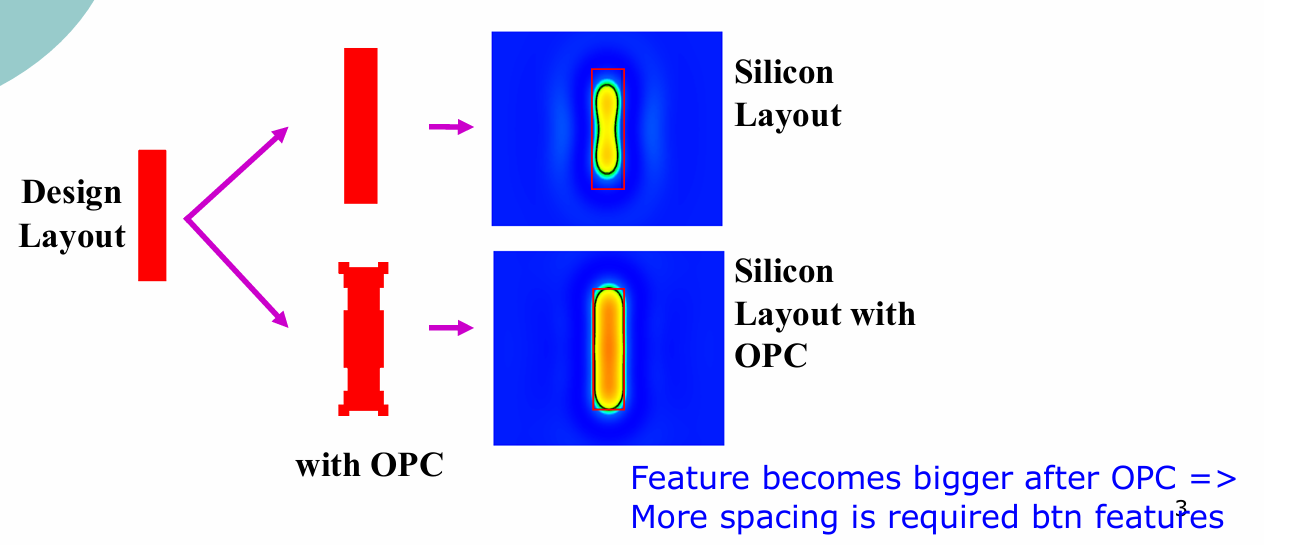
Optical Proximity Correction (OPC) 是一種 Computational Lithography 的技術,修改 mask 來補償繞射和光刻製程中的非理想效應,讓實際製造出的 Pattern 更接近設計的目標。
- OPC 會造成線寬變寬,所以要考慮
Design Rule,ex:兩條線之間要留多少空間
End-to-End Seperation Rule
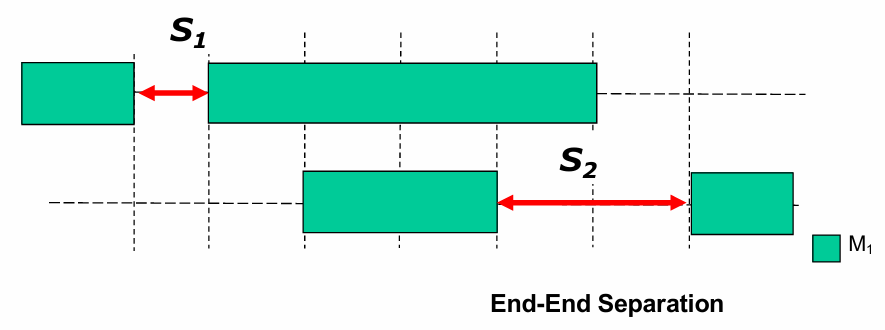
- 如果一條 Wire 的端點的相鄰軌道上有另一條 Wire,那這條 Wire 的末端至少要留 S2 的空間
- 其他情況只需要預留 S1 的空間
Minimum Length Rule
每條線至少要有多長
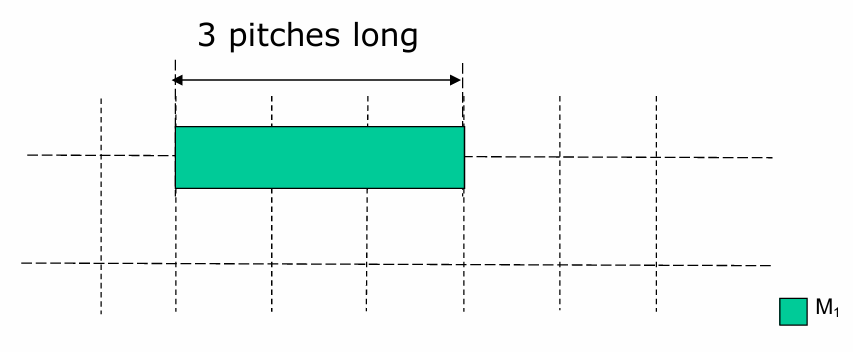
MANA (A Shortest Path MAze Algorithm under Separation and Minimum Length NAnometer Rules)
傳統的 Maze Routing Algorithm 是在 Grid 上找一條最短的路徑,可能用 BFS 或 Dijkstra 等等,但是在 VLSI 設計中,還要考慮一些 Design Rule
考慮到 Design Rule 的 Maze Routing Algorithm
Post-Processing
把找到的路徑再做一些調整,像是延伸 Wire,讓他們符合先前提到的Design Rule,不過這方法沒那麼好,會花很多資源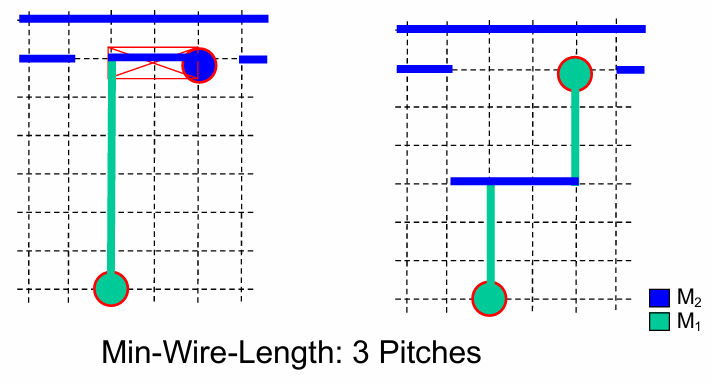
增強型 Maze Routing Algorithm
在找路徑的時候就考慮Design Rule,像是「每條 Wire 至少要有多長」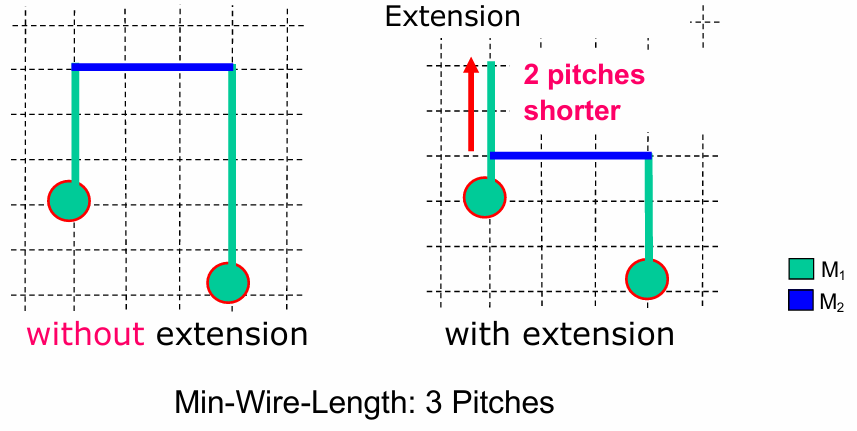
不能直接用個 L 型的 Wire,每一層要馬是水平,要馬是垂直
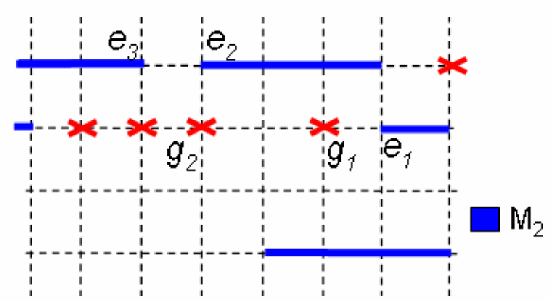
End-end separation rule handling
檢查每個 grid point,如果這個 grid point 不能滿足 End-end separation,就把它濾掉
Minimum length rule handling
在做 Maze Routing 的時候,要看這條 wire 有沒有足夠的空間做 extension
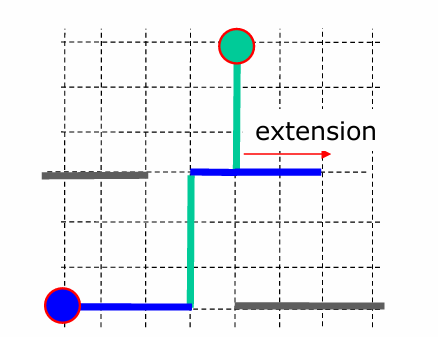
Find a Shortest Path
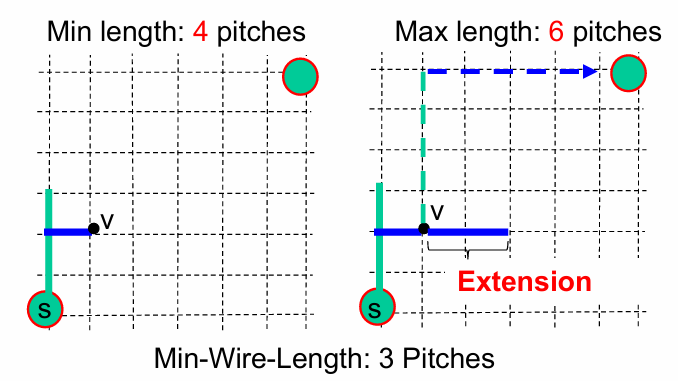
- Min Length: 全部的 wire 長度加起來,不包含最後一段的 extension
- Max Length: 全部的 wire 長度加起來,包含最後一段的 extension
Polynomial time complexity
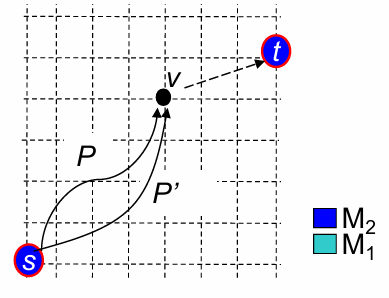
對不需要的 partial path 做 pruning,可以達到 Polynomial time complexity

像是這邊可以只保留 $P^\prime$,捨棄 $P$
Pruning Strategy
Stradgy 1
如果 $\text{minlen}(P) \geq \text{maxlen}(P^\prime)$,就捨棄 $P$
Stradgy 2
如果 $\text{maxlen}(P) = \text{maxlen}(P^\prime)$ 且 $\text{minlen}(P) = \text{minlen}(P^\prime)$,兩個一樣好,捨棄其中一個即可

Best Cost-First Expansion
Maze Routing 的演算法本質上是還是 A*-Search,要考慮某個 grid point 和 destination 的 manhattan distance,才能夠有方向性,所以
$$
\text{Cost}(P) = \text{maxlen}(P) + \text{Manhattan dist.}
$$